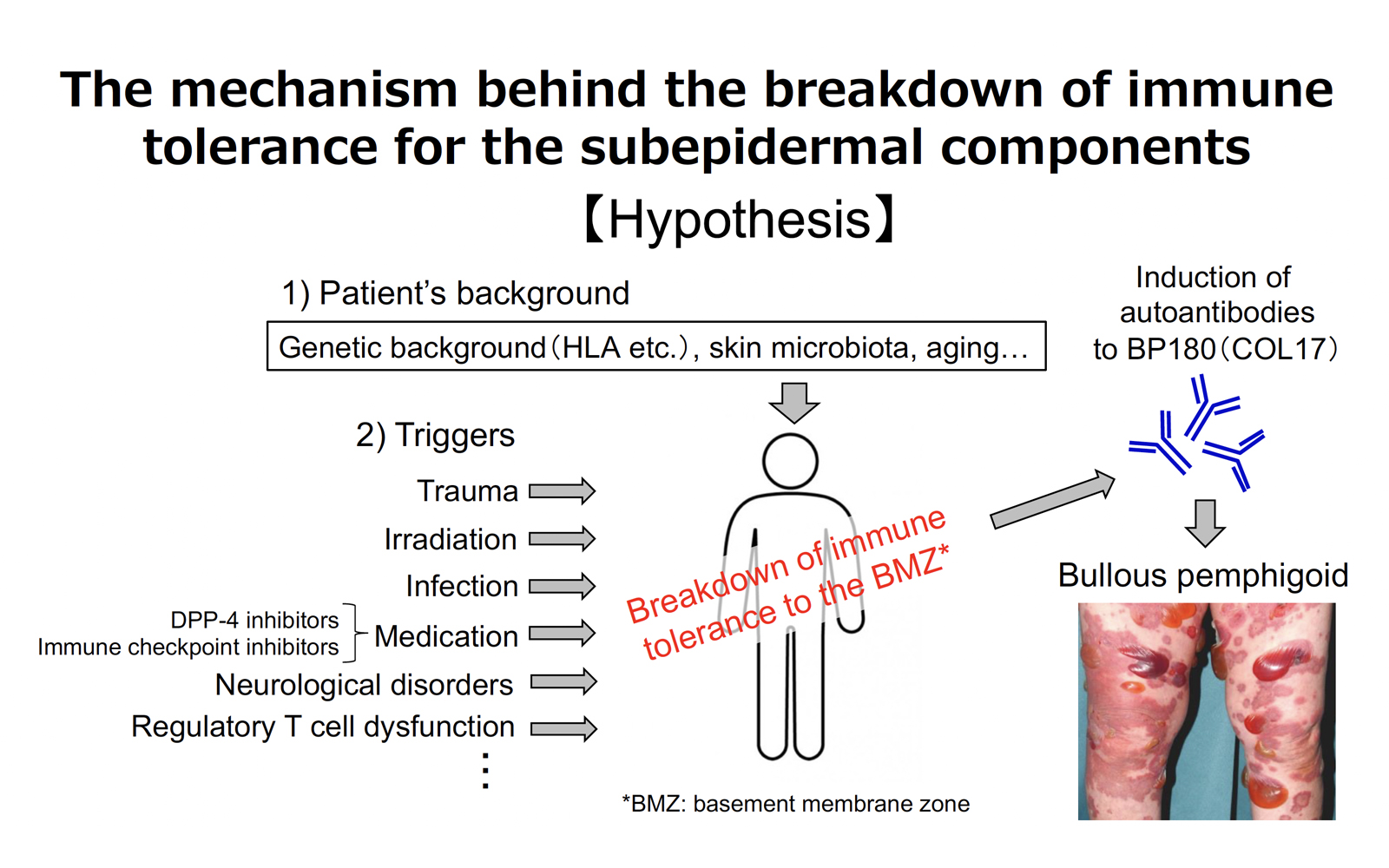
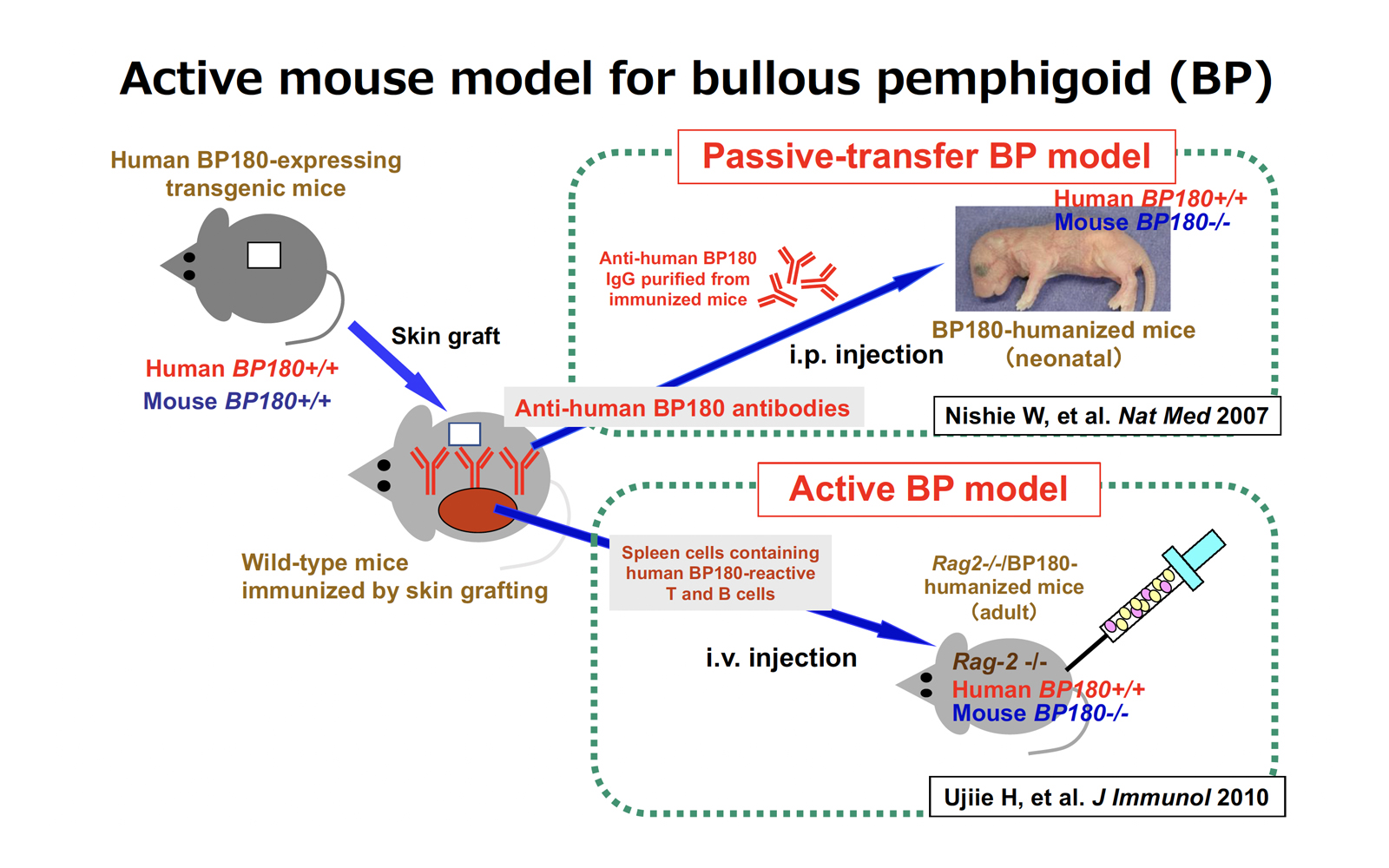
The skin immunology team is working to elucidate the mechanism of breakdown of immune tolerance in the skin using samples from aging mice, disease model animals, and patients with autoimmune blistering disease. We are also conducting research on the pathogenicity of autoreactive T lymphocytes and eosinophils in bullous pemphigoid and the pathophysiology of drug-induced pemphigoid. We also use the outpatient clinic for blistering diseases as a platform for a variety of clinical studies. In addition, we are conducting fundamental research on alopecia areata and vitiligo vulgaris. Our members are Ken Muramatsu (studying abroad), Takamasa Ito (studying abroad), Norihiro Yoshimoto, Chihiro Shiiya, and Miao Zheng. We are continuing our research every day with the aim of achieving results that can contribute to the medical care of patients with autoimmune blistering diseases, and results that approach the elucidation of the pathophysiology of autoimmune diseases.
Major research results since 2016
- γδ T Cells Protect the Liver and Lungs of Mice from Autoimmunity Induced by Scurfy Lymphocytes (Ujiie H et al. J Immunol 2016)
- A possible association between BP230-type bullous pemphigoid and dementia: a report of two cases in elderly patients (Zheng M, Ujiie H et al. Br J Dermatol 2018)
- HLA-DQB1*03:01 as a Biomarker for Genetic Susceptibility to Bullous Pemphigoid Induced by DPP-4 Inhibitors (Ujiie H et al. J Invest Dermatol 2018)
- Intravenous IgG Reduces Pathogenic Autoantibodies, Serum IL-6 Levels, and Disease Severity in Experimental Bullous Pemphigoid Models (Sasaoka T, Ujiie H et al. J Invest Dermatol 2018)
- Regulatory T-cell dysfunction induces autoantibodies to bullous pemphigoid antigens in mice and human subjects (Muramatsu K, Ujiie H et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2018)
- Autoantibodies undetectable by chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay require extended antigen-antibody reaction time for detection (Mai Y, Ujiie H et al. Br J Dermatol 2019)
- Characteristics of IgG subclasses and complement deposition in BP230-type bullous pemphigoid (Zheng M, Ujiie H et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2019)
- Immune Reaction to Type XVII Collagen Induces Intramolecular and Intermolecular Epitope Spreading in Experimental Bullous Pemphigoid Models (Ujiie H et al. Front Immunol 2019)
- Clinical and immunological features of pemphigus relapse (Ujiie I, Ujiie H et al. Br J Dermatol 2019)
- Japanese guidelines for the management of pemphigoid (including epidermolysis bullosa acquisita)(Ujiie H et al. J Dermatol 2019)
- Regulatory T cell subsets in bullous pemphigoid and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid (Muramatsu K, Ujiie H et al. J Dermatol Sci 2020)
- Clinical characteristics and outcomes of bullous pemphigoid patients with versus without oral prednisolone treatment (Ujiie I, Ujiie H et al. J Dermatol 2021)